When you’re hammering away on ChatGPT or toggling between dozens of Google Chrome tabs to get questions answered, it can be easy to forget that state-of-the-art software can’t perform its magic without the underlying hardware executing all that code.
And when it comes to the world’s most advanced software, more and more of that code is processed by NVIDIA, which holds the pole position in the Acceleration Economy list of AI Ecosystem Top 12 Pioneers. In addition to its dominant position in AI, NVIDIA recently raised eyebrows when it joined the rarified ranks (along with Microsoft and Apple) of companies with a $3 trillion market cap.
Company Background
Until about two years ago, it would have been impossible to predict that we’d be discussing NVIDIA in the same sentence with the world’s dominant tech providers. The company has been building hardware and infrastructure products since its launch in 1993. The founder and omnipresent CEO, Jensen Huang, has taken NVIDIA from a gaming company – producing chips made for high- performance game graphics – to one of the most important companies on the planet by riding the twin waves of AI and massive data center buildouts to support all those new, intensive applications.
NVIDIA currently has 29,600 employees. The company made over $60 billion in revenue in fiscal 2024, compared to roughly $27 billion in 2023 – growth of over 120%. In its fourth quarter alone, revenue grew 262% and net income grew 628%. Those aren’t exactly the kinds of growth numbers you’re accustomed to seeing from mature tech companies with tens of billions in revenue.
Explosive Growth
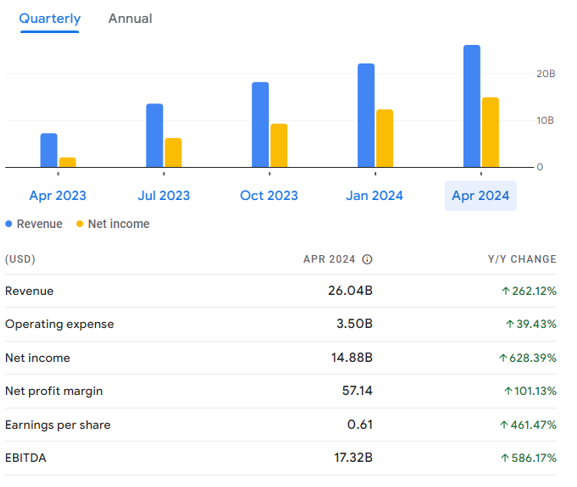
In this evolution, NVIDIA has gone beyond hardware. The company has built software and frameworks that are custom-made for its chipsets. Robust partnerships with virtually all the major technology companies in the AI ecosystem are a core part of the company’s strategy, and a huge factor in delivering its technology at an incredible scale.
Tech Innovations
NVIDIA’s products are best understood as a technology stack rather than a set of individual hardware and software components. The stack begins with GPUs and hardware that underpin its software frameworks and platforms.
NVIDIA is well known for consumer GPUs that power a wide range of PCs and high performance laptops. Less known to the average person: NVIDIA chips designed for high performance computing (HPC) — with applications in AI, data analytics, and scientific research — are also prevalent.
The best known of these is the A100 Tensor Core GPU, used in countless data centers around the world. The T4, a versatile GPU optimized for inference of machine learning (ML) models, and DGX systems, which are AI compute systems made for enterprises, are also core enterprise offerings.
The NVIDIA AI Enterprise suite is a cloud-native software platform designed for enterprises to quickly build and deploy GenAI applications. Beyond providing enterprise-level support and security, one thing that makes the AI Enterprise Suite unique is its support for various models – both NVIDIA-developed and external models — through microservices optimized for NVIDIA hardware. The company refers to it as the “operating system for enterprise AI.”
NVIDIA has many software frameworks built for its hardware:
- NVIDIA CUDA for parallel computing
- TensorRT, a deep learning inference library
- DeepStream SDK for video analytics
- NVIDIA Clara for healthcare and life-science computing workflows
- NVIDIA Jarvis for conversational AI
- NVIDIA Omniverse for 3D simulation and collaboration
- NVIDIA Merlin, an open source framework for recommender systems
The company offers AI cloud services including the NVIDIA GPU Cloud (NGC), a cloud-based optimized for AI, deep learning, and HPC containers, models, and workflows, as well as NVIDIA Base Command, a cloud-native platform for managing AI development workflows.
NVIDIA products also play a prominent role in the automotive industry. NVIDIA Jetson is an edge AI platform for autonomous machines and IoT, while NVIDIA DRIVE AGX is the platform for autonomous vehicles, including hardware, software, and AI algorithms for self-driving cars.
Ecosystem Partnerships
NVIDIA has aggressively built partnerships across the AI ecosystem to provide value to customers and bring solutions to market with maximum reach and impact.
The company supports smaller organizations through NVIDIA Inception, a startup accelerator program supporting AI startups with NVIDIA resources, and NVIDIA Education, which provides resources and education for AI developers alongside the NVIDIA Deep Learning Institute (DLI).
The NVIDIA Partner Network includes a wide range of partners such as solution providers, OEMs, distributors, and system integrators. NVIDIA offers these partners a collection of sales and marketing resources, training, and technical support to enhance their capabilities in delivering NVIDIA-based technology. NVIDIA provides a comprehensive suite of SDKs, libraries, and tools that ISVs can leverage to enhance the performance and capabilities of their applications.
NVIDIA partners with major cloud providers (AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft, Oracle) to offer NVIDIA GPUs and software in the cloud. It works closely with a wide range of enterprise software giants including Microsoft, SAP, Oracle, and ServiceNow, as well as many others.
The company has partnered directly with large firms in verticals including automotive, healthcare, manufacturing, and beyond. These diverse partnerships range from providing chipsets to collaborative development and investment, but nearly all have an element of co-creation. For example, NVIDIA worked with J&J MedTech and GE Healthcare to develop healthcare microservices that include models for drug discovery and an inference model, NVIDIA NIM, now available in the NVIDIA AI Enterprise Suite.
Customer Success: BMW
If your enterprise applications execute any HPC tasks, you’re likely using NVIDIA products. Tech giants including Amazon, Meta Platforms, Microsoft, and Alphabet are believed to be among NVIDIA’s biggest customers, making up roughly 40% of its revenue. Top AI start-ups including OpenAI and autonomous vehicle companies including Tesla are big customers.
In the auto industry, the German luxury car brand BMW collaborated with NVIDIA to implement AI-driven robotics and automation in manufacturing facilities. Utilizing NVIDIA’s tech, BMW deployed smart manufacturing solutions to improve efficiency, flexibility, and quality in their production lines. This includes computer vision systems for quality control and predictive maintenance.
BMW also selected NVIDIA’s DRIVE platform for its autonomous vehicle development. This collaboration includes using NVIDIA DRIVE AGX, an AI compute platform, to power BMW’s next-generation vehicles with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving capabilities. NVIDIA and BMW engineers work closely to co-develop and integrate AI models and algorithms necessary for self-driving cars.
The collaboration between the two firms doesn’t end there. BMW uses NVIDIA tech both in the cars, for driver assistance, and for internal use: predictive analytics in manufacturing, visualizing virtual factories or designs, high fidelity 3D renderings, using AI to optimize energy efficiency, and beyond.
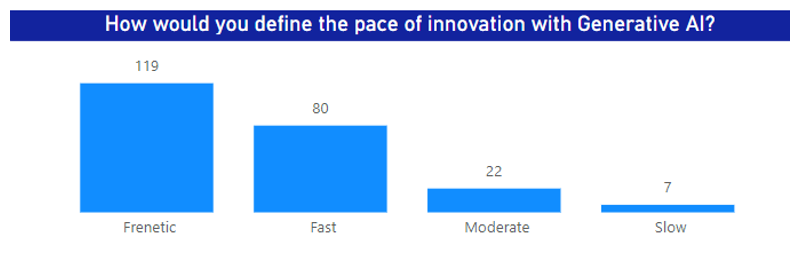
Customers including BMW rely on innovative NVIDIA hardware, software, and partnerships to help manage the relentless pace of innovation that they’re experiencing in the GenAI era. In fact, a recent Acceleration Economy survey found that 52% of respondents rated the current pace of innovation as “frenetic,” while another 35% rated that pace as “fast.” NVIDIA and many of its partners are setting that pace.
Analyst Perspective
From my perspective as an early-career, Gen Z entrepreneur, Jensen Huang sets a powerful example with his visibility at numerous AI and partner events. His presence and leadership have been a big factor in turning NVIDIA into the powerhouse it is today – all while still looking stylish in his ubiquitous leather jacket.

NVIDIA is the gatekeeper to the world of AI. If you’re a consumer needing a high-performance computer, you need NVIDIA chips. If you’re building a data center, you can guess where you’ll buy your chips. If you’re an enterprise that needs best-in-class hardware and software for advanced AI applications in your business, NVIDIA and partners deliver that. If you need any indicator of the company’s trajectory, just take a look at its stock price, which looks like it’s trying to settle on another planet.
To me, NVIDIA feels like more than just a business. Like the railroad or the printing press, the second- and third-order effects of NVIDIA infrastructure are enormous: the company has created a platform on which a new generation of companies can grow, on which new innovations in AI and high-performance computing are seeded.
Plus, NVIDIA’s playing the long game at the same time it capitalizes on today’s AI boom. The company spent $7.34 billion on R&D in 2023, a 39% increase from 2022 and nearly 30% of revenue that year.
It’s built countless ecosystem partnerships, brought dozens of major firms along for the ride, and brought the power of AI to the world. It offers a diverse product portfolio supporting customers from startups like my own up to global enterprises like BMW. From tech titans to early-stage startups, NVIDIA’s impact is felt by customers and partners across the AI Ecosystem.










