A few years ago, a fellow CIO reached out to me for advice on choosing between two cybersecurity-managed service providers. Since my company had experience working with both providers, I could offer a fair comparison. After discussing her company’s options, she mentioned that her company was likely going with provider X, primarily because it claimed to use artificial intelligence (AI) in its product, while the other company didn’t mention the technology at all. She didn’t have much additional information, but the AI aspect appeared to be a significant differentiator in her company’s decision-making process.
This experience stayed with me, and as AI has gained prominence, it raises a question: Is AI genuinely a crucial component of a cybersecurity technology offering, or is it merely a buzzword that companies use to attract potential customers?
To hear practitioner and platform insights on how solutions such as ChatGPT will impact the future of work, customer experience, data strategy, and cybersecurity, make sure to register for your on-demand pass to Acceleration Economy’s Generative AI Digital Summit.
Cybersecurity With and Without AI
Indeed, AI does play a vital role in today’s cybersecurity technology. However, it’s essential to grasp how AI is effectively employed in cybersecurity to make informed choices when selecting a technology product or provider. I took a look at several cybersecurity technology features that I have worked with for years and looked into how incorporating AI into them might enhance their effectiveness. Here’s what I found:
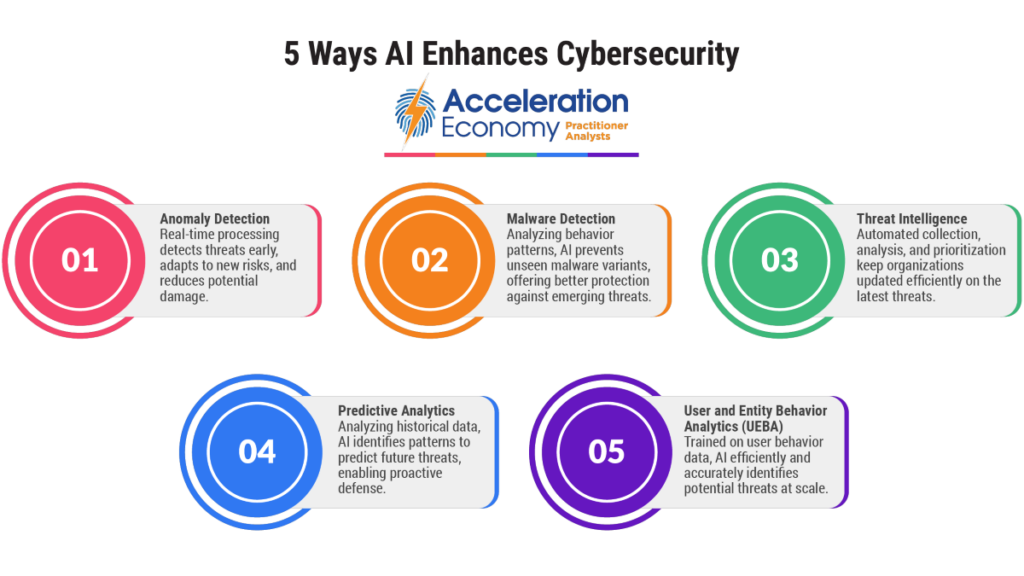
1. Anomaly Detection
Without AI: Security analysts manually monitor logs, network traffic, and system behavior, relying on predefined rules and thresholds to identify anomalies. This process can be time-consuming and may not catch new or evolving threats. Whenever I see demos of rule-based software, I think: “Who is ever going to have time to sit and write all these rules manually?”
With AI: AI can process massive amounts of data in real time, detecting threats early and reducing potential damage. AI can identify new and evolving threats more effectively than manual methods. As a CIO with a small staff, I need the cybersecurity software we use to constantly adapt to the threat landscape automatically, without my team having to constantly configure it.
2. Malware Detection and Prevention
Without AI: Traditional antivirus solutions rely on signature-based detection, which requires constant updates to identify new malware variants. This approach is very reactive. Someone has to have already found the malware, identified it, and provided an update that mitigates the threat.
With AI: AI-powered solutions can analyze file characteristics and behavior patterns to detect and prevent malware, including previously unseen variants. AI offers better protection against emerging threats. This is one benefit that gives me peace of mind, because I am much more concerned about a brand new threat that doesn’t match any known signature. Technology that can detect these zero-day threats, as they are often called, is crucial.
3. Threat Intelligence
Without AI: Security analysts gather and analyze threat intelligence from various sources manually, which can be time-consuming and might miss crucial information. There are many good threat intelligence sources — mostly services and news outlets — that you can subscribe to. However, the prospect of sifting through all of them to try and determine which ones were relevant to my company in an era when even the threats themselves are increasingly AI-supported, seems daunting and offers diminishing returns.
With AI: AI can automatically collect, analyze, and prioritize threat intelligence, helping organizations stay updated on the latest threats and improve their security posture more efficiently. This is what AI is good at, and getting better at: sifting through large amounts of data and quickly determining what information is relevant to my needs.
4. Predictive Analytics
Without AI: Security teams rely on historical trends and expert judgment to predict future threats, which may not accurately anticipate new attack vectors.
With AI: AI can analyze historical data and identify patterns to predict future threats, enabling proactive defense and more effective resource allocation. The bad actors are constantly trying to stay ahead of the defensive technology. It is critical that the software be able to predict the next move rather than just react based on historical trends.
5. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
Without AI: Identifying insider threats or compromised accounts may involve manual monitoring and analysis, which can be labor-intensive and less effective. I’ve tried to think of all the different ways that a user might “do something unexpected” and it is a very complicated process.
With AI: Because it’s been trained on so much user and entity behavior data, AI can monitor and analyze user and entity behavior patterns more efficiently and accurately identify potential threats, and at scale. It is much better to let the software learn what “expected” behavior looks like, so anything outside of that can raise a flag.
What to Look for in an AI Cybersecurity Provider
AI offers numerous enhancements to existing cybersecurity technology and practices, and the features mentioned above serve as a solid foundation for a requirements list. However, when considering potential providers for your AI cybersecurity transformation, it’s crucial to ask them how their technology addresses these aforementioned aspects, not to mention the following:
- Integration and compatibility: Ensure that the vendor’s AI-driven cybersecurity solutions can be seamlessly integrated with your existing IT infrastructure, security tools, and processes. Compatibility with current systems is crucial for a smooth implementation and maximum effectiveness. It can be discouraging to find out after you have purchased a solution that it doesn’t “play well” with the rest of your technology stack.
- Data privacy and compliance: Ensure the vendor adheres to data privacy regulations and industry standards applicable to your organization. AI-driven cybersecurity solutions may process large amounts of sensitive data, so it’s crucial to verify that the vendor has robust data protection policies and practices in place.
- Training and support: Assess the vendor’s commitment to providing training, support, and resources for your organization. This includes understanding how it will help you manage the AI-driven cybersecurity solutions, as well as provide ongoing support for any issues or questions that may arise.
- Transparency and explainability: Assess the vendor’s commitment to providing transparent and explainable AI solutions. This is important for understanding the reasoning behind AI-generated decisions and maintaining accountability within your organization. I think this may be difficult for some providers, as they may be afraid to divulge too many details of how their technology works. Even if you encounter resistance, it’s important to find out as much as you can.
- Continuous improvement: Ensure that the vendor is committed to continuously auditing and improving their AI models and algorithms, as well as staying updated on the latest advancements in AI and cybersecurity. We’ve seen how rapidly AI technology has progressed recently. There’s no excuse for any provider to refrain from making its technology better.

Which companies are the most important vendors in cybersecurity? Check out
the Acceleration Economy Cybersecurity
Top 10 Shortlist.
Final Thoughts
AI has become a vital component of effective cybersecurity strategies, offering numerous advantages over traditional approaches. By understanding the ways that AI can enhance security measures and considering key factors when selecting a provider, organizations can harness the technology’s ability to better protect their digital assets and stay ahead of emerging threats. As a CIO, recognizing the importance of AI in cybersecurity and making informed decisions is not only crucial for the success of your organization, but also a testament to your commitment to staying at the forefront of technological advancements.
This article has been updated since it was originally published on April 26, 2023.