The following is an excerpt by Acceleration Economy Analyst, Bill Doerrfeld which appeared in the Future Office of the CFO edition of the Acceleration Economy Journal. The September 2021 issue addressed the role executives play in technology investments, how automation architecture impacts business processes, developing partnerships for optimal business continuity, cybersecurity and risk mitigations, the importance of deep analytical skills, and much more.
Cyber security is in the zeitgeist—and for a good reason. High-profile breaches continue to make headlines, on a near-daily basis. These attacks harm brand image and take time and
resources to remediate. To make matters worse, the exposure of sensitive data could break compliances and lead to fines, class-action lawsuits, and hefty settlement sums. If left unchecked, vulnerable data and software pose a serious financial threat.
To get an idea of the severity, consider the onslaught of large-scale attacks in recent years. Most infamous is the 2017 Equifax breach, in which 143 million user accounts were compromised, exposing personal information and 200,000 credit card numbers. In 2014, Morgan Chase leaked personal data from 76 million households and 7 million small businesses. Most recently, a hacker group targeting Accenture demanded $50 million in a ransomware attack on 6 TB of data.
A company losing access to its internal data can bring operations to a grinding halt. But it’s not just data under threat; computing environments are vulnerable too. As more companies turn to the public cloud, their infrastructure becomes more prone to misconfigurations and attacks. For example, in 2018 it was discovered that hackers had carefully infiltrated a Tesla computing node running on Amazon Web Services, and were using it to mine cryptocurrency, an act known as cryptojacking.
All cases above underscore the financial imperative to encourage a security-first culture throughout your organization. Below, I’ll highlight some of the top trends impacting cyber security that CFOs should be aware of. Cyber security is a broad landscape, and solutions are just as complex. But I’ll attempt to list some general practices that will bolster prevention efforts and forecast where the future of cyber security is heading.
Trends Impacting Cyber Security & Finance
What are the biggest trends impacting cyber security and financial data? Undoubtedly, ransomware, man-in-the-middle attacks, and data breaches are rising threats. But, what factors are causing this influx? To answer this, let’s consider the elements at play in 2021.
The value of data is rising.
First off, data is more valuable than ever. Digital experiences soared as a major touchpoint for all businesses during the pandemic. Now, reliant upon these interfaces, the data they touch has grown in importance as well. Of these, personal financial data is a hot commodity for hackers.
Organizations face surmounting user privacy concerns.
Organizations must respond to many new user data privacy regulations that affect the use of personal data, including GDPR, CCPA, HIPPA, and others. Without the proper data handling, especially of sensitive private data in healthcare and financial services, companies could easily break compliances when transacting across geographical boundaries.
The open banking movement is going global.
On the theme of regulations, significant legislation is dictating banks to open up financial data for interoperability with third-party FinTechs. We now have PSD2 in Europe, UK Open Banking, CDR in Australia, and Open Banking Brazil. Canadian and US banks are opening up through market pressure as well. As financial institutions become more composable, they require a more elaborate security posture.
Connectivity and integrations are in the spotlight.
Many businesses are seeing benefits in platformification. This often entails offering web-based integrations to data and infrastructure for others to develop upon. Most modern IT departments have also shifted from a monolithic codebase to embrace decoupled microservices, which depend upon connections with external resources to function. These trends all depend upon application programming interfaces (APIs) as a standard communication style. As a result, Gartner predicts that by 2022, API attacks will become the most frequent attack vector.
Incorrect authorization is a top integration concern.
Organizations are not adequately prepared for this newfound API reliance. Salt Labs reports a 300% increase in malicious API traffic in the last six months. Of all API-based attacks, OWASP ranks Broken Object Level Authorization as the most common vulnerability. For many APIs, HTTP calls can easily be manipulated by hackers to gain unauthorized access.
Misconfigurations and insecure defaults are top cloud-native threats. In an effort to increase scalability and universal reach of software offerings, more technology is becoming cloud-based. Software operators are also moving to modern, cloud-native infrastructure like containerization and Kubernetes to achieve rapid deployment. However, if not used correctly, cloud-native tools could suffer from insecure defaults, misconfigurations, and visibility issues.
Top 5 Cyber Security Mitigations for CFOs
So, how can a financial leader protect their critical data? Here are five preventative measures, that if followed, should greatly increase your cyber security footing:
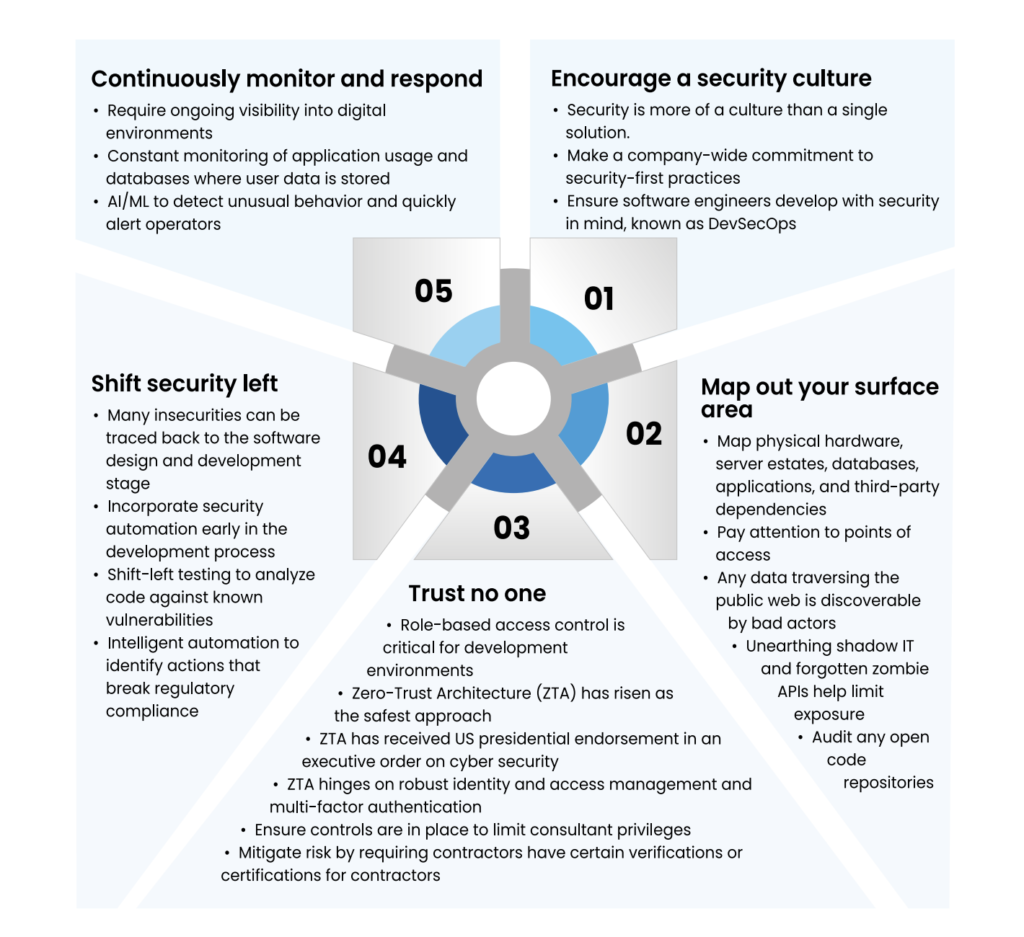
As one can see, cyber security is an area that truly impacts all areas of IT business. Depending on the company size, it might make sense to create a Cyber Security Center of Excellence (CCoE) to research best practices and disseminate security knowledge across an organization.
Cyber Security Vendors
Financial data requires financial-grade security. Therefore, it’s usually not a recommended best practice to build out your own security solutions. Security requirements are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and exploits are being discovered on a daily basis. Many cyber security vendors have also invested in valuable AI/ML capabilities to advance threat detection and prevention.
So, who are the top vendors in the cyber security realm? The cyber security solution market is broad, where the remedies are just as extensive as the threats themselves. In 2020, CFO ranked the top 10 financial security solution companies as Cognive, Intrusion, NMI, Q Net Security, Secure Insight, Axonius, comforte AG, SafeGard Cyber, Secureworks, and VERA. These solutions span everything from encryption to penetration testing, network monitoring, compliance auditing, and enforcing runtime security policies. These services can be very helpful to neutralize threats or block suspicious IP addresses, for example. Some even offer hardware to create more of a tangible firewall, which could be necessary for high-risk data.
When shopping for cyber security solutions, it’s important to consider tools built upon open standards. This ensures the companies are engaging with the broader community to adjust their offerings as new vulnerabilities emerge. In terms of identity and access management, vendors like Curity, Okta, and Ping Identity are viable options. Furthermore, cyber security solutions must also support a cloud-native world. Since API integrations are projected to be under much scrutiny in the years to come, it is an ideal time to invest in API security protection. Salt Security, Moesif, API Fortress, and Kong are all examples of vendors that are highly focused on testing, monitoring, and securing integrations within this new paradigm.
Tomorrow’s Cyber Security Footing
Cyber security is definitely an area to watch closely. As are the financial implications of inaction, since every vulnerability presents a potential expense. Thus, CFOs should take a role in ensuring their executive teams are encouraging secure practices. As financial personal data and banking functionality are intriguing to profit-seeking hackers, this is a top area to protect.
Financial security is also an area destined for further evolution. As more and more enterprises invest millions into cryptocurrency and adopt smart contracts with blockchain, the threat spectrum will inevitably encompass these new technologies as well. Integrations are also sure to come under more scrutiny as financial services embrace platform models that connect with other businesses and expose their data and infrastructure in the process.
Lastly, it’s good to remember that not all insecurities arise from highly sophisticated attacks. Oftentimes breaches occur due to simple social engineering tactics. With all that in mind, now is an ideal time to audit your cyber security efforts. Otherwise, it may not be that long until you see an all too familiar name on tomorrow’s data breach headline.







